Series: Getting into D2C eCommerce SEO > Episode 6: How does organic search work?
So how does organic search work?
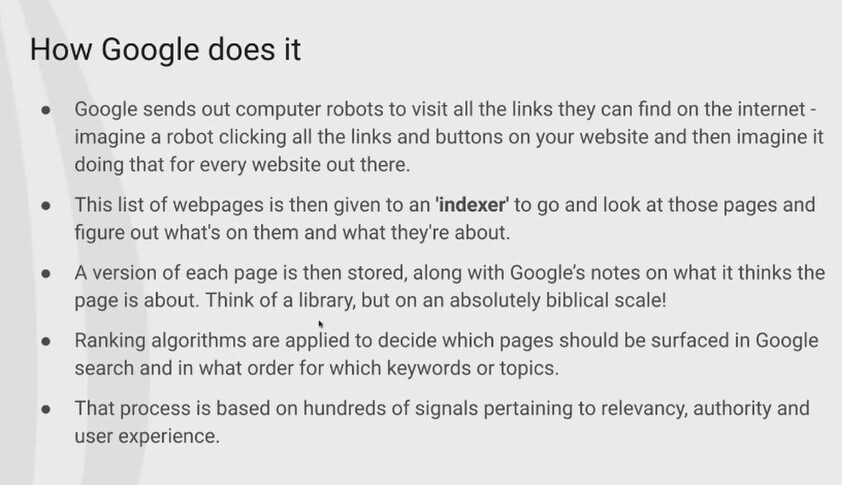
A search engines job is effectively going out, finding all the web pages out there, organising it in some fashion and then when someone searches for something, give them the most relevant piece of information back. Give them the most relevant page back. That's its job. That's what it's trying to do.
If it does that exceptionally well, it can sell adverts and be very successful. Case in point - Google.
However, given that the Internet is a mind bogglingly large place in terms of number of web pages and information and all the rest of it, we have to create systems of automation, and so on, in order to be able to achieve that goal.
So Google has several pieces of technology, so we're distill it down and make it as simple as we can.
Googlebot
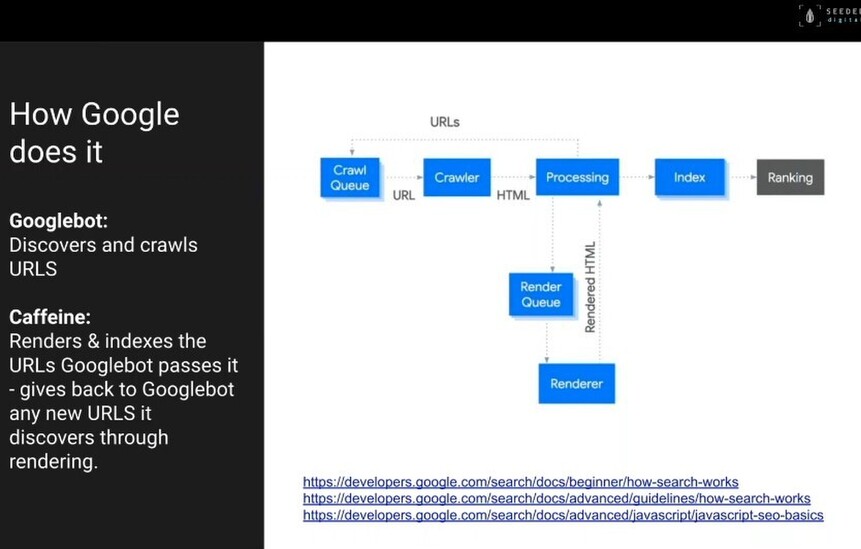
The first piece of technology of Googlebot and Googlebot is what we call a crawler.
That crawler is sent out into the Wild West of the Internet, and goes and finds links. It likes links.
It'll arrive at, for example, your homepage, and it will find all the links on the page, all the links is what it is interested in. It just wants the links.
And it'll put those in a list. And it will then follow all those links and it will find another page, and another page, and another page, and it will look at all the links on those pages.
And it will grab all those links and adds them to the list, and that's what it does!
It just grabs links, finds more links and puts them in an enormous list. An enormous, ongoing list.
This is happening all the time. It's just constantly doing this. So it's creating that huge list.
So that's the crawl. Googlebot discovers and crawls URLs. That's it job.
That list is then passed on to the whimsically named caffeine, which is the name of Google's index.
We hope you're enjoying our series on "Getting into D2C eCommerce SEO" and if If you'd like to sign-up to receive this sort of content from us into your inbox, then you can do that with the form at the bottom of this page.
Caffeine
Caffeine is the name of Google's indexer.
So what the index it does is it takes that list of URLs that has been generated by the crawler, and it goes and says right - show me what you have got.
And it goes and grabs all the HTML and it renders it and says, "Oh, I see the text on here. That's great. I can see everything on the page. Brilliant, Right."
What it will then do is potentially if your website hasn't shown all the links in the first place, if there's more to then find, once it renders all that information, if more links come out at that point, it will then pass those links back to Googlebot, come in and have another pass at that.
And off we go again and back in. So there is this process and interplay, and it's ongoing.
Googlebot is generating lists of URLs, and caffeine is in their rendering the results.
And so once those results have been rendered, those results then get put into Google's index.
So you're not searching the native internet
Sometimes it is a bit of a revelation to people, but when you're searching Google, you're not actually searching the naive Internet of everything that's out there, you're searching Google's copy of it.
Google is a website, it's got all this information, and it's presenting you that information, just as you would go on our website and you click on the menus and whatever else. It's their version of what's out there.
So basically, all of that rendered content needs to be arranged and put into an index.
So we're starting to think now about a library on a sort of a biblical scale, in terms of how the books are organised. And then you have an indexation system to go and access them, and they might be notes around the indexation system to say this book is on this particular topic area and is covered in this area over here etc. There is this indexation that goes inside the rendered pages.
So the rendered pages go into the library, Google's index, and then they go in there with a whole bunch of other information, which Google pulls from the page.
So it then starts passing over as it processes the language on there. It looks at the assets, looks at the targeting, so then effectively creates its own crib sheet for each page that it finds.
And that then helps with the next process, so that it's at this point that all of those pages, all those millions that are pages that are in there, then have the ranking algorithms run over the top.
So that's when you hear about all these sort of hundreds of signals that Google uses for ranking, that's what is happening.
At this point, the webpage, YOUR webpage, has passed through this system.
And from that, it's, deemed OK.
Google will go "Well, this page is about this thing, and I think it's relevant to that subject, and its authority around that subject is this Good. And, therefore, I will rank it in this position when someone searches for the key term pertain to this page."
That's pretty much it, in terms of what's involved.
It's a multi-stage process, where you get from your putting content out there, to Google accessing it and ranking it effectively, and the signals involved and so on and so forth.
Sign-up to receive this sort of content in your inbox
By filling out this form and clicking 'Sign up' you're giving us permission to email you with our marketing material (this kind of stuff is our marketing material). You'll be able to unsubscribe at any time via any of the emails we send, and we'll not be passing your data to any third parties... because we're not dicks. We're hoping that's something you can live with. Thank you so much for checking out our content - we really appreciate it.